One of the most concerning narratives for any democratic country is the extent to which sub-populations of its citizenry are “living in the shadows”. Living in the shadows or social exclusion (i.e. lack of access to a state identification card, bank accounts, and healthcare) is the process in which individuals are reluctant to fully engage in public life in order to avoid scrutiny because of their minority status (ethnicity, citizenship, religious beliefs, and/or sexual orientation). In this analysis, we examine Latino populations who are living in the shadows within the United States, and to the extent to which they may be avoiding public life because they do not want to be discriminated against due to their citizenship status, and/or the citizenship status of their loved ones.
For this discussion we rely on the groundbreaking National Latino Health and Immigration Survey, a new survey sponsored by the RWJF Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico and implemented by Latino Decisions. We recently showcased this data-set on a webinar for the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s Human Capital Network blog as well as a previous post here showcasing the content more focused on the Affordable Care Act.
The survey of 1,505 Latino adults was fielded from January 29, 2015, to March 12, 2015, and provides some of the most comprehensive data on Latinos’ attitudes related to health care and immigration in the ACA era. Although there is tremendous depth to this study we focus specifically on questions that address the notion of “living in the shadows.”
Are Latinos Living in the Shadows?
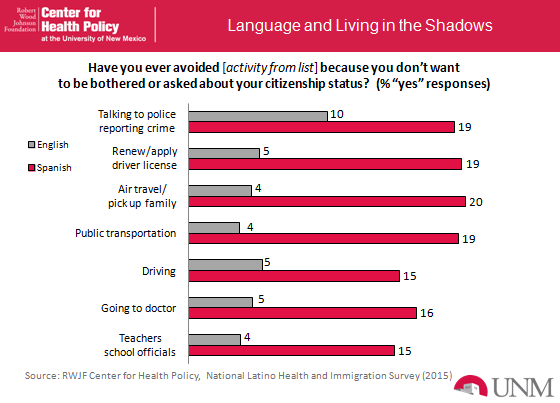
The question that we wanted to pursue within this line of inquiry is essentially how many Latinos are ‘living in the shadows” and among Latinos who is most likely to be reluctant to step out of the shadows and fully engage in public life? To get at this we started by simply asking: “Have you ever avoided the following activities because you don’t want to be bothered or asked about your citizenship status?” We asked specifically about daily life activities like taking public transportation, renewing or applying for a driver’s license, talking with teachers and school officials, reporting crime to police, and visiting a doctor or clinic.
Results from the survey indicate that the majority of Latinos, 70 percent overall, are not concerned by inquiries about their immigration status. This outcome makes sense given that the majority of sample is comprised of U.S. citizens, and among non-citizens, most are lawful permanent residents. Nevertheless, we do find evidence that a substantial share of Latinos do report adjusting aspects of their day-to-day life because they do not want to be bothered or asked about their citizenship status. In fact, we learned that overall, about 7 percent of Latino adults shy away from contact with educators, 9 percent avoid taking public transportation, 9 percent steer clear of visiting health care providers, and 13 percent pass on reporting crime to police (see figure below).

One of the most important sources of variation in this battery is language use. As illustrated below, we find that Spanish dominant Latinos (58% of the sample) are more likely to avoid common activities due to fears of being harassed about their immigration status. More specifically, 15 percent of Spanish dominant Latinos responded that they avoided contact with educators, 19 percent avoided taking public transportation, 16 percent avoided going to a doctor, and 19 percent avoided reporting crime to the police because they did not want to be bothered or asked about their citizenship status. These results signal a deep-rooted problem in our society and should be of concern for public servants and health care service delivery personnel interested in eliminating social and health disparities.
What does immigration mean for Latino access to health care?
Given our emphasis on the health care sector, we consider how our findings impact the community of stakeholders in this industry. Looking at the average count of self-reported visits to health care providers, we find that those living in the shadows — measured as having avoided at least one of the activities that we ask about — systematically report fewer health care visits. This contrast appears sharpest for Latinos who are 30-34 years old, precisely the age demographic most needed in the risk pool to make health insurance through the ACA affordable for everyone.
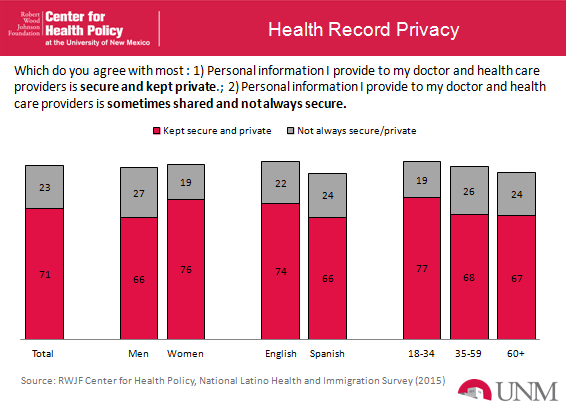
Another important component of this survey is that we are able to provide perspective on an important question: does fear of being tracked by the government for immigration reasons impact Latino take-up of health insurance through the ACA marketplaces or exchanges. We know that privacy and sharing personal information was a concern raised by many Latinos during the healthcare.gov launch. The administration directly addressed this very concern in President Obama’s March 2014 interview with Telemundo and Univision. He assured Latinos that healthcare.gov and CuidadoDeSalud.com are not used to collect information for immigration enforcement agencies, such as U.S. Immigration Customs and Enforcement. To assess how Latinos perceive the security of their private health information, we asked respondents which statement they agree with more:
1) Personal information I provide to my doctor and health care providers is secure and kept private; or
2) Personal information I provide to my doctor and health care providers is sometimes shared and not always secure.
Approximately 23 percent of respondents stated that the personal information they provide their doctors and health care providers is sometimes shared and not always secure. There are some sources of variation however. As you can see in the figure below, there is a gender difference, with men being more likely to believe that information may not always be kept secure/private. More in line with the in-the-shadows framework, if respondents personally know someone who has been detained or deported (36 percent of the sample), the sentiment that personal information is not secure rises to 29 percent. These results suggest that the externalities and consequences of immigration enforcement through mass deportation are spilling over to the health care arena, and undermine much of the hard work going into the administration’s signature domestic policy program.
One of the key lessons that we have gleaned from our investigation based on the 2015 National Latino Health and Immigration Survey is that Latinos may not view government as compartmentalized by policy area. Their lived experience is much more complex. Latinos are simultaneously the targets of two of the largest bureaucratic developments in history, one charged with the provision of health care, the other ramped for the purpose of enforcing immigration law.
There is already clear indication that health care practitioners are customizing their outreach and delivery systems to address the spill-over effects of immigration to health care provision. This is a wise approach because the daily lives of many Latino patients are located at the intersection of the immigration and health policy streams. Our research team is pursuing several studies to test the relationship between living in the shadows and the rich battery of health indicators in this dataset. We have found a clear relationship between knowing an undocumented immigrant or someone detained or deported and poorer health across several measures. [1] Whether policy makers and immigration enforcement officials modify their approach to take into account the collateral impact of their policies on the health of their fellow countrymen and women remains an open question.
For better or worse, the take-away from our study is that immigration policy is health policy, and health policy is immigration policy. This is directly in line with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s new priority of establishing a culture of health, where health and well-being is thought of comprehensively. Our findings suggests the need for public servants (teachers, police officers, school administrators) and health care providers to better understand the role social stigma plays in pushing hard to reach populations in the shadows to better engage our collective concerted effort to reduce health disparities.
[1] Vargas, Edward D., Gabriel Sanchez and Melina Juarez “Investigation of Latino’s Perceptions of Immigration Policy and Health Outcomes.” Paper presented at the annual meeting of the 2015 Western Political Science Association, Las Vegas, Nevada.
Gabriel R. Sanchez is an associate professor of political science at the University of New Mexico, the executive director of the RWJF Center for Health Policy at UNM, and the director of research for Latino Decisions.
Francisco I. Pedraza is an assistant professor of political science at Texas A&M University and is a recent alumnus of the Robert Wood Johnson Scholars in Health Policy Research Program at the University of Michigan.
Edward D. Vargas is a postdoctoral scholar at the Center for Women’s Health and Health Disparities Research in the School of Medicine and Public Health at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Survey Methodology: Latino Decisions surveyed a representative sample of 1,005 Latino adults in the United States between January 29th and March 12th of 2015 over the telephone. An additional 400 interviews were completed online. Surveys were implemented to randomly selected phone numbers and conducted via live, person-to-person (i.e. not robocalls) phone calls. Respondents were reached on a combination of both landline (65%) and mobile phones (35%). Interviews were conducted in English or Spanish, according to the respondent’s choice. All interviewers were fully bilingual. The survey carries a margin of error of +/-3.1 percent points and was approximately 22 minutes in length.